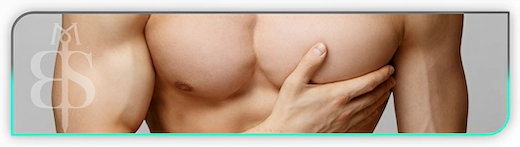
At your Gynecomastia surgery consultation with Mr. Taimur Shoaib at Berkeley Square Medical, the process is structured to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of your condition, a clear understanding of the treatment options, and a personalised approach to surgery.
Introduction & Medical History Review
- Initial Greeting: You will meet Mr. Taimur Shoaib in-person at your consultation, a highly experienced consultant plastic surgeon, who will introduce himself and discuss the purpose of the consultation.
- Medical Questionnaire: You’ll be asked about your general health, previous surgeries, any medications you’re currently taking, and lifestyle factors such as smoking or alcohol consumption.
- Gynecomastia-Specific History: Mr. Shoaib will inquire about the onset, duration, and any potential causes of your gynecomastia (hormonal imbalances, medication side effects, weight changes, etc.).
- Relevant Symptoms: You’ll be asked about associated symptoms like tenderness, pain, or psychological effects of living with gynecomastia.
Physical Examination
- Breast Tissue Examination: Mr. Shoaib will perform a physical exam to assess the extent of the glandular tissue and fat deposits in the chest area.
- Chest and Skin Assessment: He will check for the presence of excess skin, the elasticity of the skin, and whether there is any sagging or stretching that may need addressing during surgery.
- Muscle and Asymmetry Check: He will examine the underlying pectoral muscles and note any asymmetry in breast size or shape.
- Additional Testing (if required): In some cases, additional tests like blood work, hormonal tests, or imaging (e.g., ultrasound or mammography) may be recommended if the cause of gynecomastia is unclear.
Discussion of Surgery Options
- Explanation of Gynecomastia Grades: Mr. Shoaib will explain the different grades of gynecomastia (mild, moderate, or severe) and how they apply to your case.
- Treatment Options:
- Liposuction: For patients with primarily fatty tissue, liposuction may be sufficient to contour the chest.
- Excision Surgery: If glandular tissue is present, Mr. Shoaib may recommend surgical excision to remove the excess breast tissue.
- Combined Approach: In some cases, both liposuction and excision are necessary to achieve optimal results.
- Skin Tightening Consideration: If there is excess or loose skin, Mr. Shoaib will discuss whether skin removal or tightening techniques are needed to enhance the final contour of the chest.
Surgical Procedure Explanation
- Procedure Details: He will explain the specific surgical techniques he will use, where incisions will be placed (usually around the areola), and the expected duration of the surgery.
- Anaesthesia: You will be informed whether the surgery will be performed under local or general anaesthesia, depending on the complexity of the case.
- Expected Outcomes: He will provide an assessment of the expected outcome, including potential improvements in chest contour and symmetry.
Risks and Complications
- Surgical Risks: Mr. Shoaib will inform you about potential risks and complications associated with gynecomastia surgery, such as bleeding, infection, scarring, or asymmetry.
- Postoperative Sensations: He will discuss sensations like numbness or tightness that may occur after the surgery and their expected recovery timeline.
- Long-Term Results: He will explain the likelihood of recurrence and factors that could affect long-term outcomes, such as weight changes or hormonal fluctuations.
Before-and-After Photos
- Gallery Viewing: Our clinical team will be happy to show you before-and-after photos of previous patients who have undergone gynecomastia surgery to give you a realistic idea of potential results.
- Personalization: He will highlight cases that are similar to yours, explaining how the techniques used can be tailored to your specific anatomy.
Recovery Process and Aftercare
- Postoperative Care: Mr. Shoaib will discuss the recovery process, including the use of compression garments, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
- Healing Time: He will explain the typical recovery timeline, including when you can return to work, resume exercise, and see the final results.
- Scar Management: He will provide guidance on scar care and options for minimizing scarring, such as silicone sheets or topical treatments.
Cost and Financing
- Detailed Cost Breakdown: The consultation that follows with our Clinical Team will include a discussion about the costs associated with gynecomastia surgery, including the journey through your treatment from consultation to your final results.
Final Q&A Session
- Addressing Your Concerns: At the end of the consultation, you will have the opportunity to ask any remaining questions, clarify doubts, or express concerns regarding the surgery, recovery, or expected outcomes.
- Personalised Plan: Mr. Shoaib will summarize the consultation, providing you with a personalised surgical plan that is tailored to your goals and medical needs.
Scheduling Surgery (if you decide to proceed)
- Scheduling the Surgery: If you decide to move forward, you can book your surgery date at this point. You’ll also receive preoperative instructions and information about what to do in the weeks leading up to the surgery.
- Further Consultation (if needed): If you need more time to decide or have additional questions, follow-up consultations can be arranged.
This consultation process ensures that patients are well-informed and confident about their decision to proceed with gynecomastia surgery under Mr. Taimur Shoaib’s expert care at Berkeley Square Medical.
Let me know if you’d like more details about any specific part of this process!
Gynecomastia surgery at Berkeley Square Medical is performed by multi-award-winning consultant plastic surgeon, Mr. Taimur Shoaib. It involves a well-structured, carefully planned procedure to achieve the best results. Here’s a detailed step-by-step breakdown of what happens during your surgery:
Preoperative Preparations
- Arrival at the Hospital: On the day of surgery, you will arrive at Berkeley Square Medical Hospital at the scheduled time. You will be greeted by the medical team and taken to a preoperative area.
- Final Consult with Surgeon: You’ll have a meeting with Mr. Shoaib where he will review the surgical plan, confirm details such as the areas to be treated, and answer any further questions.
- Marking the Surgical Area: The surgeon will make precise markings on your chest while you’re standing or sitting. These markings guide the surgical incisions and define the areas for tissue removal.
- Anesthesia Consultation: You’ll meet our Consultant Anaesthetist, who will explain the type of anaesthesia you’ll receive (either general or local anaesthesia with sedation). This ensures you won’t feel any pain during the surgery.
Anesthesia Administration
- Sedation or General Anesthesia: Once in the operating room, the Anaesthetist team will administer anaesthesia. General anaesthesia puts you into a deep sleep, while local anaesthesia with sedation keeps you relaxed but awake.
- Monitoring: Throughout the surgery, your vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels) are closely monitored to ensure your safety.
Surgical Procedure
The specific steps of gynecomastia surgery depend on the technique used (liposuction, excision, or a combination). Here’s how each step generally progresses:
Liposuction (For Fat Removal)
If the gynecomastia consists mostly of excess fat, liposuction is usually the primary approach.
- Incision Placement: Small incisions (2-4 mm) are made, usually at the edge of the areola or in the natural chest crease, to minimize visible scarring.
- Tumescent Solution Injection: A sterile solution (containing saline, lidocaine for pain relief, and epinephrine to reduce bleeding) is injected into the chest area. This helps to loosen the fat and makes it easier to remove.
- Fat Removal: A thin cannula (a hollow tube) is inserted through the incisions, and the surgeon uses controlled movements to break up and suction out the excess fat. Liposuction is ideal for contouring the chest and smoothing the overall appearance.
Excision (For Glandular Tissue Removal)
If there is significant glandular breast tissue, excision surgery is required.
- Incision Around the Areola: The surgeon makes an incision around the edge of the areola (periareolar incision). This approach allows for discrete scarring.
- Glandular Tissue Removal: Through the incision, the surgeon carefully excises (removes) the dense glandular tissue responsible for the male breast enlargement. This step is critical for achieving a flat chest.
- Excess Skin Removal (if needed): In cases of severe gynecomastia or if there is sagging skin, the surgeon may also remove excess skin to prevent drooping and improve chest firmness.
Combination of Liposuction and Excision
- Liposuction Followed by Excision: In many cases, both fat and glandular tissue are present. The surgeon first uses liposuction to remove fat, then proceeds with the excision of glandular tissue to achieve a balanced, contoured chest.
Shaping and Symmetry Check
- Final Contouring: After removing the necessary tissue, Mr. Shoaib will assess the symmetry and shape of the chest. He may make additional adjustments to ensure a natural, masculine contour.
- Areola Reduction (if required): In some cases, gynecomastia surgery includes reducing the size of the areola (the pigmented area around the nipple) for better proportionality with the newly contoured chest.
- Hemostasis: The surgeon will ensure that any small blood vessels are cauterized (sealed) to minimize bleeding.
Closing the Incisions
- Internal Sutures: Dissolvable sutures may be placed inside the chest to secure the tissue and help maintain the new chest shape.
- Skin Closure: The incisions are carefully closed using fine, dissolvable stitches or sutures to promote minimal scarring. In some cases, adhesive strips or skin glue may be used.
- Dressing: Sterile dressings are applied over the incisions, and a compression garment is usually placed around the chest to reduce swelling and help the skin adhere to the underlying tissue.
Postoperative Care in the Hospital
- Monitoring in Recovery Room: After the surgery, you will be moved to a recovery area where you’ll be monitored as the effects of anaesthesia wear off. The medical team will ensure that you’re comfortable and that pain is managed effectively.
- Compression Garment: You will be fitted with a compression vest that must be worn for several weeks. This helps reduce swelling, supports healing, and encourages a smooth, even chest contour.
- Initial Recovery: Most patients can go home the same day (outpatient procedure) unless the case is complex or general anaesthesia is used, in which case an overnight stay might be required.
Postoperative Instructions
- Pain Management: You’ll be prescribed pain medications to manage any discomfort during the first few days. Over-the-counter medications may be recommended for mild pain.
- Wound Care: Instructions for caring for your incisions will be provided, including when to change dressings and how to keep the area clean to prevent infection.
- Activity Restrictions: You’ll be advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks. Gentle walking is encouraged to promote blood circulation.
- Follow-Up Appointments: A follow-up visit is usually scheduled within a week to check on your healing progress and remove any non-dissolvable stitches, if used.
Recovery at Home
- First Few Days: You can expect swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort for a few days post-surgery. Keeping the compression vest on and following aftercare instructions is critical to minimize swelling.
- Gradual Resumption of Activity: Most patients can return to non-strenuous work within a week, but physical activities, especially those involving the chest muscles, should be avoided for 4-6 weeks.
- Healing and Final Results: The majority of swelling subsides within a few weeks, but it may take 3-6 months to see the final results as your chest continues to heal and settle into its new shape.
Final Results and Long-Term Care
- Scarring: Over time, scars will fade and become less noticeable. The team may recommend scar treatments such as silicone sheets or laser therapy to reduce visibility.
- Permanent Results: The results of gynecomastia surgery are generally permanent, especially if the underlying cause is addressed (e.g., hormone imbalances or medications that led to gynecomastia). Maintaining a stable weight is essential for preserving the chest contour.
Final Follow-Up
- Long-Term Checkups: You may have additional follow-up visits with Mr. Shoaib to monitor your progress and address any concerns. These checkups ensure that your healing is on track and that you are satisfied with your results.
The entire process is designed to ensure safety, comfort, and satisfaction with the aesthetic and physical outcomes of the surgery.
Aftercare following gynecomastia surgery at Berkeley Square Medical is a critical part of the process to ensure smooth recovery, minimize complications, and achieve optimal results.
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
Recovery Room
- Monitoring After Surgery: Once your surgery is complete, you will be taken to the recovery room, where the medical staff will monitor your vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels) as you wake up from anaesthesia. The team will ensure you are comfortable and that immediate post-surgical needs are met.
- Pain Management: If you experience discomfort or pain, medication will be administered to manage it. Mr. Taimur Shoaib and the anesthesiologist will have tailored a pain relief plan based on the complexity of the surgery.
- Observation Time: Depending on whether you had local or general anaesthesia, you’ll stay in the recovery room for a few hours. Most gynecomastia surgeries are outpatient, meaning you can go home the same day once the medical team is satisfied with your recovery.
Discharge
- Post-Surgery Instructions: Before you are discharged, you’ll receive a detailed set of aftercare instructions. This will include how to care for your incisions, guidelines for activity levels, and medication schedules.
- Compression Garment: You will be fitted with a compression vest or bandage around your chest, which is crucial for minimizing swelling and helping the skin adhere properly to the underlying tissue. You will be instructed to wear this garment for several weeks, almost continuously.
- Transportation Home: Since you will likely be groggy from anaesthesia, you will need someone to drive you home after surgery.
First 24-48 Hours Post-Surgery
Rest and Limited Movement
- Rest: The first 24-48 hours should be spent resting, preferably in a semi-upright position to reduce swelling. You may experience mild discomfort, tightness, and swelling in the chest area, but this is normal.
- Movement: Gentle walking is encouraged to promote circulation and prevent blood clots, but any strenuous activity should be avoided.
Pain and Swelling Management
- Pain Medication: You will be prescribed painkillers or advised to take over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen to manage any discomfort.
- Ice Packs: Applying cold compresses or ice packs to the chest area (over the compression garment) can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort. Be sure to follow the hospital’s guidelines on the frequency and duration of cold therapy.
Hydration and Diet
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out the anaesthesia and assist in your body’s healing process.
- Light Meals: Stick to a light diet initially, as nausea from anaesthesia is common. Gradually return to your normal eating routine.
First Week Post-Surgery
Wound Care
- Dressing Changes: You may have specific dressings over the incision sites. The medical team will explain how and when to change these dressings. It’s important to keep the area clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Incision Inspection: Check your incisions for any signs of infection, such as excessive redness, warmth, swelling, or unusual discharge. If any of these symptoms occur, contact Berkeley Square Medical immediately.
Compression Garment
- Continuous Use: The compression vest should be worn day and night, except when showering. This garment helps reduce swelling, support the healing tissues, and ensures the chest contours develop correctly.
Showering
- Showering Instructions: Typically, you will be allowed to shower 2-3 days post-surgery, depending on the type of dressings and sutures used. You will be instructed to keep the water pressure low and avoid soaking the incision sites. Be gentle when drying the area.
Activity Restrictions
- Avoiding Strain: Avoid any activity that puts strain on your upper body, such as lifting heavy objects, pushing, pulling, or engaging in intense physical activity.
- Walking: Gentle walking is encouraged to aid circulation and reduce the risk of blood clots, but any form of cardio or weight training should be avoided for at least 4-6 weeks.
One-Week Follow-Up Appointment
A. First Check-Up
- Visit to the Clinic: You will typically have a follow-up appointment scheduled within the first week after surgery. During this visit, a member of our medical team will check your incisions, remove or replace dressings, and ensure that your recovery is on track.
- Suture Removal: If dissolvable sutures were not used, the stitches will be removed at this appointment. This is a quick and usually painless process.
- Compression Garment Adjustment: The fit of the compression garment may be adjusted, and you’ll be reminded to continue wearing it as instructed.
2-4 Weeks Post-Surgery
Reduced Swelling and Bruising
- Decreasing Swelling: By the end of the second week, swelling and bruising will start to subside significantly, though some residual swelling may persist for a few more weeks.
- Wearing the Compression Garment: Continue to wear the compression vest full-time (day and night) during the first 4 weeks. In some cases, you may be instructed to wear it during the day only after 3-4 weeks.
Scar Care
- Scar Healing: Mr. Shoaib may recommend scar treatments such as silicone sheets, topical gels, or laser therapy to minimize the appearance of scars. Keep the area moisturized and protected from the sun.
- Massage: After a few weeks, you may be advised to start gentle massaging of the chest to soften the tissues and promote even healing.
Gradual Return to Activity
- Light Activities: By week 2-4, you may begin to resume light daily activities, but still avoid any upper-body exercises or heavy lifting.
- Driving: You may be cleared to drive once you are no longer on strong pain medications and can comfortably wear the seatbelt across your chest.
6-12 Weeks Post-Surgery
Further Follow-Up Appointment
- Second Check-Up: You will likely have another follow-up with Mr. Shoaib around the 4-6 week mark. At this visit, he will assess how your healing is progressing and address any concerns you may have.
- Discontinuing the Compression Garment: Depending on your progress, you may be allowed to stop wearing the compression garment or reduce its use to daytime only.
Resuming Physical Activity
- Gradual Return to Exercise: Around the 6-week mark, you may be cleared to slowly reintroduce physical exercise, starting with lower body workouts and light cardio. Upper-body exercises, such as chest workouts, should still be avoided for another few weeks.
- Avoiding Chest Strain: Be careful not to overexert yourself, and listen to your body as you ease back into a fitness routine.
3-6 Month Long-Term Recovery & Final Results
Final Healing
- Swelling Resolution: The majority of swelling will have subsided by the 6-week mark, but it can take up to 3-6 months for the chest to fully heal and the final results to become apparent.
- Tissue Settling: Your chest contours will gradually improve over time as the tissues settle and heal.
Scar Maturation
- Scar Fading: Scars will continue to fade over the next several months. Follow your surgeon’s advice on scar treatments to help minimize their appearance.
Long-Term Follow-Up
- Final Check-Up: You may have a final follow-up scheduled several months post-surgery to assess your long-term results.
- Lifestyle Maintenance: To maintain your results, it’s important to keep a stable weight and avoid factors that could trigger recurrences, such as certain medications or hormone imbalances.
Potential Complications to Watch For
While complications are rare, it’s important to be aware of any signs of problems during your recovery, such as:
- Infection: Redness, warmth, fever, or unusual drainage from the incision site.
- Seroma or Hematoma: Fluid accumulation or excessive swelling in the chest.
- Persistent Pain: If pain doesn’t improve with medication or worsens over time.
- Asymmetry: If the chest appears uneven after healing.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should contact Berkeley Square Medical immediately.
Conclusion
The aftercare process for gynecomastia surgery at Berkeley Square Medical is designed to ensure a smooth recovery, minimize complications, and maximize aesthetic outcomes. Following Mr. Shoaib’s aftercare instructions carefully and attending all follow-up appointments are essential for achieving the best possible results.
Gynecomastia surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries certain risks and potential complications. While the surgery is generally safe when performed by an experienced surgeon such as Mr. Taimur Shoaib at Berkeley Square Medical, it’s important to be aware of the risks associated with the procedure. Here’s a detailed step-by-step breakdown of the risks involved:
1. Anaesthesia-Related Risks
Gynecomastia surgery typically involves general anaesthesia or local anaesthesia with sedation, both of which carry some risks.
- General Anesthesia Risks:
- Adverse Reactions: Some patients may experience allergic reactions to the anaesthesia, which could cause breathing difficulties, heart irregularities, or other complications.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common side effects of general anaesthesia include nausea and vomiting, which usually subside within the first 24 hours post-surgery.
- Sore Throat: If a breathing tube is used, you might experience a sore throat after surgery.
- Rare Complications: In very rare cases, serious complications like respiratory issues or cardiac arrest can occur.
- Local Anesthesia with Sedation Risks:
- Over-Sedation: If sedation is too strong, it can lead to breathing difficulties.
- Discomfort: Some patients may feel light discomfort if the local anaesthesia does not fully numb the surgical area.
2. Infection
Postoperative infections are a risk with any surgery, including gynecomastia surgery. This can occur at the incision sites or within the tissues under the skin.
- Signs of Infection:
- Redness, warmth, or swelling around the incision.
- Discharge of pus or fluid from the wound.
- Fever or chills.
- Prevention: The use of antibiotics during and after the procedure helps reduce this risk. Additionally, keeping the surgical area clean and following post-surgical care instructions will minimize the likelihood of infection.
- Treatment: If an infection does occur, it is usually treatable with oral or intravenous antibiotics, but in more severe cases, surgical drainage may be required.
3. Bleeding (Hematoma)
A hematoma is the pooling of blood under the skin, which can occur after surgery.
- Signs:
- Sudden swelling, firmness, or bruising in the chest area.
- Discoloration or changes in skin tone around the surgical site.
- Risks:
- Hematomas may increase the risk of infection and delay healing.
- In some cases, a second surgery may be required to drain the accumulated blood.
- Prevention: Following the surgeon’s advice on activity restrictions and wearing the compression garment correctly can help prevent excessive bleeding or hematoma formation.
4. Seroma (Fluid Accumulation)
A seroma is the collection of fluid under the skin, which can occur after tissue is removed.
- Signs:
- Noticeable fluid-filled pockets under the skin.
- Swelling or discomfort in the chest area.
- Risks:
- Seromas can delay healing and increase the risk of infection.
- Treatment: Small seromas may resolve on their own, while larger ones may require draining by the surgeon using a needle.
5. Scarring
Scarring is a natural part of any surgical procedure, and gynecomastia surgery is no exception.
- Types of Scarring:
- Hypertrophic Scarring: Raised, red scars that stay within the boundaries of the incision.
- Keloid Scarring: Raised scars that extend beyond the incision and can grow over time. These are more common in individuals with darker skin tones.
- Prevention: To minimize the appearance of scars, surgeons typically place incisions in discreet locations, such as around the areola or in the natural chest creases. Additionally, following post-surgical care instructions, such as using silicone scar sheets or scar creams, can help reduce scarring.
- Treatment: If scars become problematic or cosmetically undesirable, treatments like laser therapy, steroid injections, or surgical scar revision can be performed.
6. Asymmetry
Post-surgical asymmetry refers to uneven chest contours, where one side may appear different from the other.
- Causes:
- Incomplete removal of glandular tissue or fat.
- Uneven skin retraction post-surgery.
- Pre-existing asymmetry that wasn’t fully addressed during surgery.
- Risks: Minor asymmetry is common and may resolve as swelling subsides. However, more noticeable asymmetry may require revision surgery.
- Prevention: Surgeons take great care during surgery to ensure symmetrical results, but individual healing patterns and tissue responses can vary.
7. Nipple and Areola Complications
Gynecomastia surgery involves working around the nipple and areola, which can lead to specific complications.
- Nipple Necrosis (Tissue Death): This is a rare but serious complication where the blood supply to the nipple or areola is compromised, leading to tissue death.
- Signs: Darkening of the nipple, loss of sensation, or hardening of the tissue.
- Treatment: Depending on the severity, minor cases may heal on their own, while severe cases may require reconstructive surgery.
- Changes in Nipple Sensation:
- Numbness: Some patients experience temporary or permanent numbness in the nipple or surrounding chest area due to nerve damage.
- Hypersensitivity: Others may develop heightened sensitivity around the nipple, which usually subsides over time.
- Prevention: Surgeons take care to preserve as much of the nipple’s nerve supply as possible, but some changes in sensation may be unavoidable.
8. Poor Wound Healing
Some patients may experience poor wound healing, where the incisions take longer than expected to close or heal.
- Risk Factors:
- Smoking.
- Poor nutrition.
- Diabetes or other health conditions that affect blood flow and tissue repair.
- Signs:
- Slow or incomplete closure of the incision site.
- Gaps or separation in the wound.
- Prolonged redness or discharge from the incision.
- Treatment: In cases of delayed healing, the surgeon may use special dressings or recommend supplements to aid the healing process. Additional surgery might be required to close the wound properly.
9. Contour Irregularities
Some patients may develop contour irregularities such as dimpling, indentations, or uneven surfaces on the chest.
- Causes:
- Over-aggressive liposuction.
- Uneven skin retraction.
- Removal of too much or too little tissue.
- Risks: This can result in an uneven or less natural-looking chest contour.
- Treatment: Minor contour irregularities may resolve as swelling decreases. More severe cases may require revision surgery or fat grafting to smooth out the chest contour.
10. Fat Necrosis (Fat Cell Death)
Fat necrosis is the death of fat cells in the treated area, which can lead to hard lumps or nodules under the skin.
- Signs:
- Firm or hardened areas under the skin.
- Lumps that can be felt when pressing on the chest.
- Risks: These lumps are typically benign, but they can be aesthetically unappealing or uncomfortable.
- Treatment: In most cases, fat necrosis resolves on its own over time. If the lumps persist, they may need to be removed surgically.
11. Allergic Reactions
Patients may have allergic reactions to medications, surgical dressings, or materials used during the procedure.
- Signs:
- Skin rash, itching, or swelling at the incision site or elsewhere.
- Treatment: Allergic reactions are generally mild and can be treated with antihistamines. In rare cases, a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) could occur, requiring emergency treatment.
12. Psychological Impact
In some cases, patients may experience emotional or psychological challenges post-surgery.
- Body Image Concerns: Even if the surgery is technically successful, some patients may be dissatisfied with the results due to unrealistic expectations or personal body image issues.
- Post-Surgery Depression: It’s not uncommon for patients to feel a temporary dip in mood during recovery, particularly if they experience discomfort, swelling, or visible scarring.
- Support: Discussing expectations and potential outcomes thoroughly with the surgeon beforehand can help mitigate post-surgical dissatisfaction. In some cases, counselling or support groups may be beneficial.
13. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) or Pulmonary Embolism
Surgical patients, especially those under general anaesthesia, are at a slight risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT), where blood clots form in the deep veins, typically in the legs. If a clot breaks free, it can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition.
- Prevention:
- Early mobilization (gentle walking) after surgery.
- Wearing compression stockings.
- In some cases, the surgeon may recommend blood-thinning medications post-surgery.
Conclusion
While gynecomastia surgery is generally safe and effective, it is important to understand the associated risks. By choosing an experienced surgeon like Mr. Taimur Shoaib at Berkeley Square Medical, you can reduce many of these